If you’re a manager at a business that lends to consumers or otherwise extends credit, you certainly are aware that 10-15% of your current customers and prospective future customers are among the approximately 27 million consumers who are now – or will soon be — fitting another bill into their monthly budgets. Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, the government issued a pause on federal student loan payments and interest. Now that the payment pause has expired, millions of Americans face a new bill averaging more than $200. Will they pay you first?
If this is your concern, you aren’t alone: Experian recently held a webinar that discussed how the end of the student loan pause might affect businesses. When we surveyed the webinar attendees, nearly 3 out of 4 responses included Risk Management as a main concerns now.
Another top concern is about credit scores. Lenders and investors use credit scores – bureau scores such FICO® or VantageScore® credit score or custom credit scores proprietary to their institution – to predict credit default risk. The risk managers at those companies want to know to what extent they can continue to rely on those scores as Federal student loan payments come due and consumers experience payment shock. I’ve analyzed a large and statistically meaningful sample (10% of the US consumer population in Experian’s Ascend Sandbox) to shed some light on that question. As background information, the average consumer with student loans had lower scores before the pandemic than the average of the general population. One of my Experian colleagues has explored some of the reasons at https://www.experian.com/blogs/ask-experian/research/average-student-loan-payments).
Here are some of the things we can learn from comparing the credit data of the two groups of people. I looked at a period from 2019 and from 2023 to see how things have changed:
- Average credit scores increased during the pandemic, continuing a long-term trend during which more Americans have been willing and able to meet all their obligations.
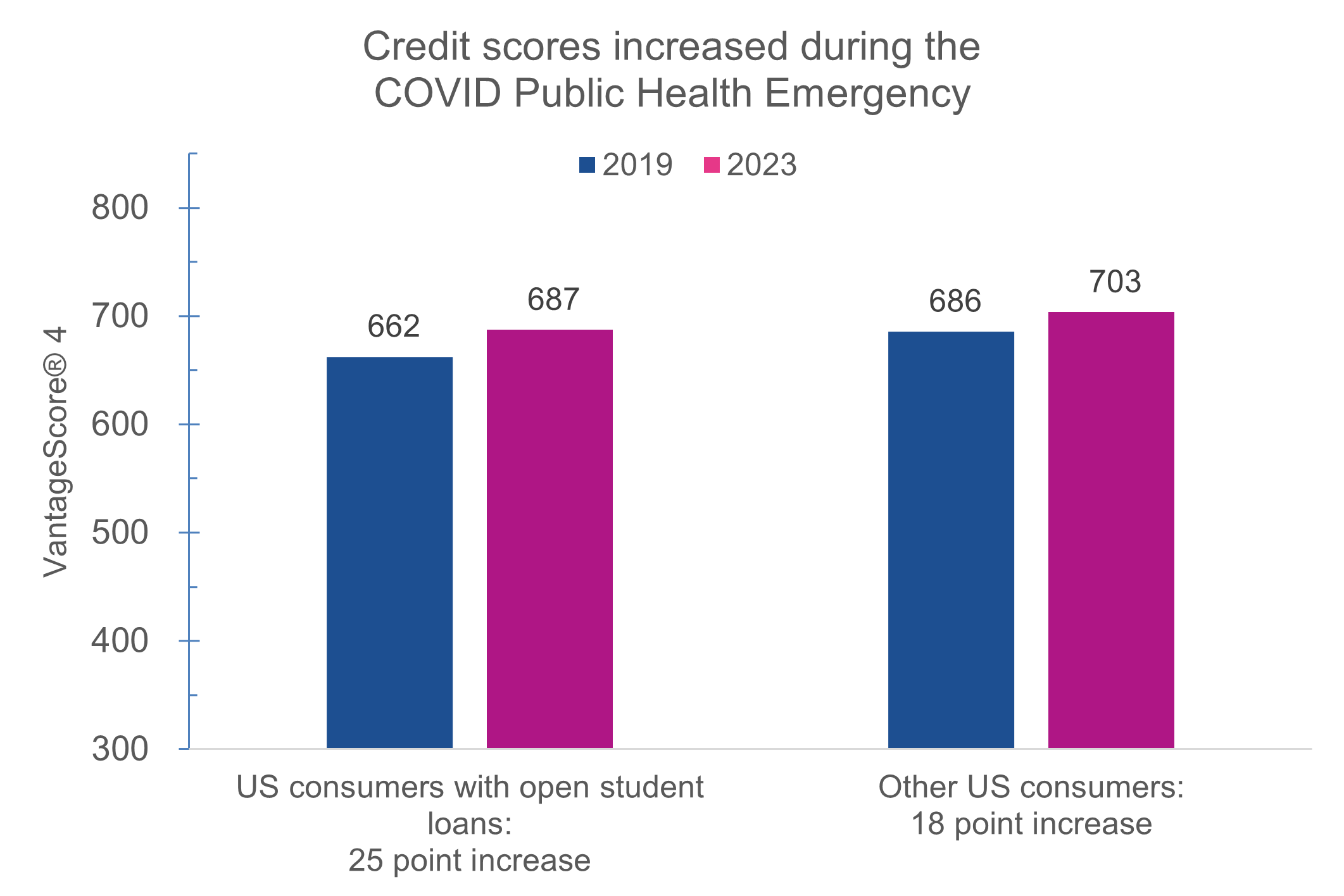
- During the COVID Public Health Emergency, consumers with student loans brought up their scores by an average of 25 points; that was 7 points more than consumers without student loans.
- Another way to look at it: in 2019, consumers with student loans had credit scores 23 points lower than consumers without. By 2023, that difference had shrunk to 16 points. Experian research shows that there will be little immediate impact on credit scores when the new bills come due.
Time will tell whether these increased credit scores accurately reflect a reduction in the risk that consumers will default on other bills such as auto loans or bankcards soon, even as some people fit student loan bills into their budgets. It is well-known that many people saved money during the public health emergency. Since then, the personal savings rate has fallen from a pandemic high of 32% to levels between 3% and 5% this year – lower than at any point since the 2009 recession. In an October 2023 Experian survey, only 36% of borrowers said they either set aside funds or they planned using other financial strategies specifically for the resumption of their student loan payments. Additional findings from that study can be found here.
Furthermore, there are changes in the way your customers have used their credit cards over the last four years:
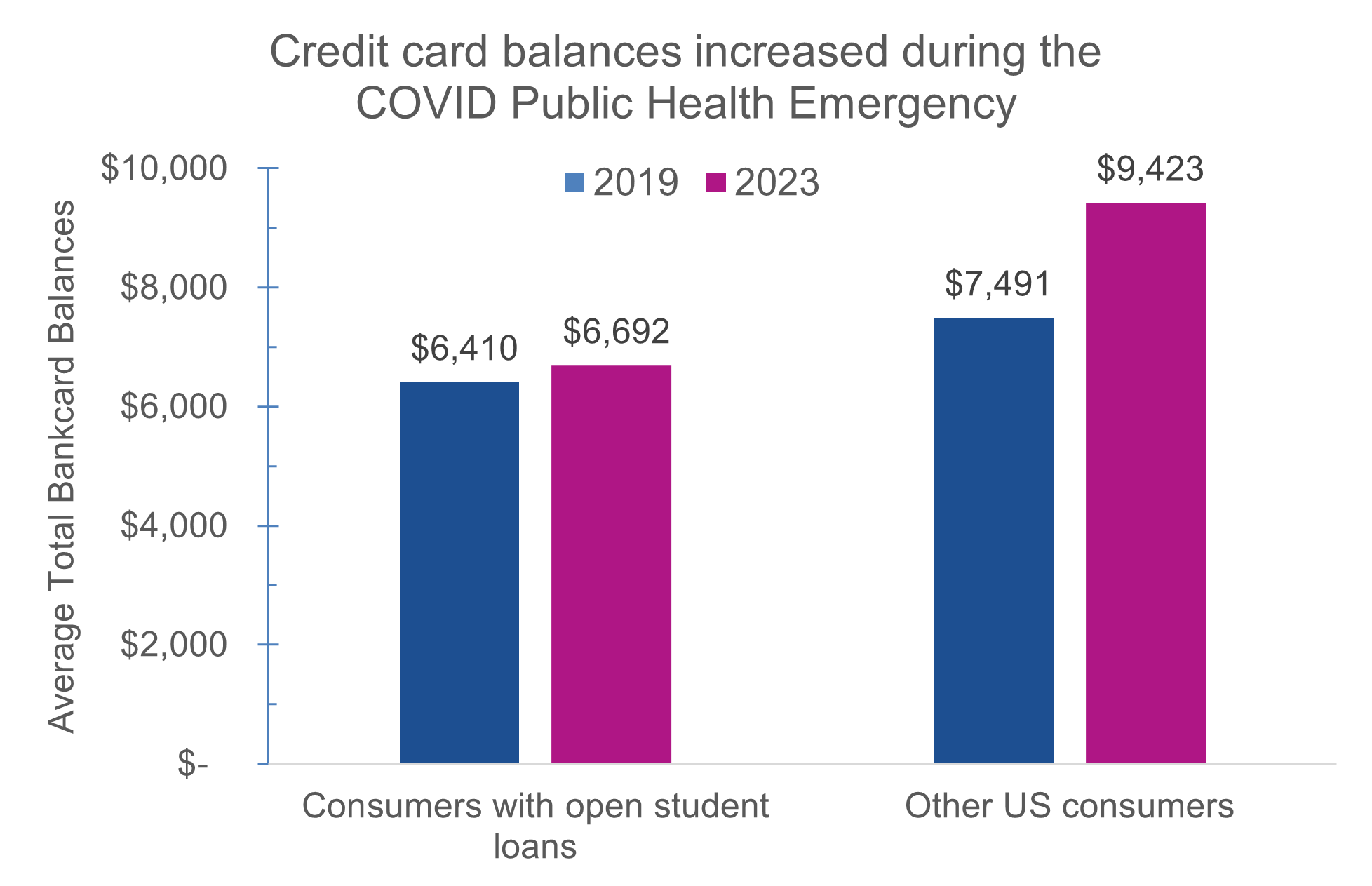
- Consumers’ credit card balances have increased over the last four years.
- Consumers with student loans have balances that are on average $282 (4%) more now than in 2019.
- That is a significantly smaller increase than for consumers without student loans, whose total credit card debt increased by an average of $1,932 (26%).
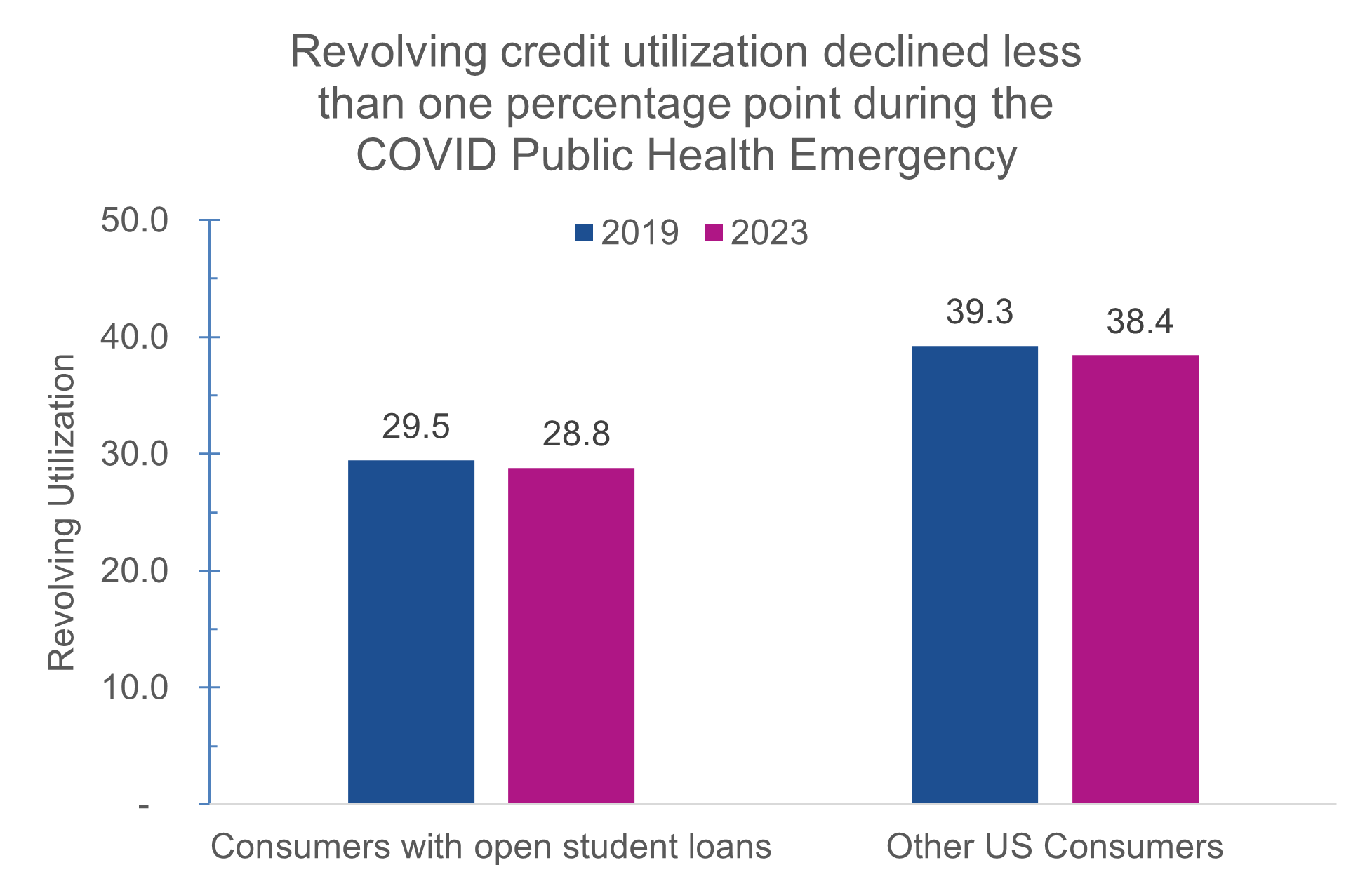
Although their balances increased, the ratio of consumers’ total revolving debt balances to their credit limits (utilization) changed by less than 1% for both consumers with student loans and consumers without. In 2019, the utilization ratio was 9.8 percentage points lower for consumers with student loans than consumers without. Four years later, the difference is nearly the same (9.6 points).
We can conclude that many student loan borrowers have been very responsible with credit during the Public Health Emergency. They may have been more mindful of their credit situation, and some may have planned for the day when their student loan payments will be due.
As the student loan pause come to an end, there are a few things that lenders and other businesses should be doing to be ready:
- Even if you are not a student loan lender, it is important to stay on top of the rapidly evolving student loan environment. It affects many of your customers, and your business with them needs to adapt.
- Anticipate that fraudsters and abusers of credit will be creative now: periods of change create opportunities for them and you should be one step ahead.
- Build optimized strategies in marketing, account opening, and servicing. Consider using machine learning to make more accurate predictions.
- Those strategies should reflect trends in payments, balances, and utilization; older credit scores look at a single point in time.
- Continually refresh data about your customers—including their credit scores and important attributes related to payments, balances, and utilization patterns.
- Look for alternative data that will give you a leg up on the competition.
In the coming weeks and months, Experian’s data scientists will monitor measures of performance of the scores and attributes that you depend on in your data-driven strategies — particularly focusing on the Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) statistics that will show changes in the predictive power of each score and attribute. (If you are a data-driven business, your data science team or a trusted partner should be doing the same thing with a more specific look at your customer base and business strategies.)
In future reports and blog posts, we’ll shed light on the impact student loans are having on your customers and on your business. In the meantime, for more information about how to use data and advanced analytics to grow while controlling costs and risks, all while staying in compliance and providing a good customer experience, visit our website.


